Introduction Wire bonding Battery Packs
This is Technology that links battery cells in parallel to conductors using wire bonds that act as fuses in the event of an overcurrent condition in the battery. To protect the wire bonds in the case of a larger overcurrent condition, a fuse may be added in series to the parallel battery cells.
Utrasonic wirebonding is used in the production of battery packs for the following connections : cell to cell, cell to busbar, cell to PCB. Typically round battery cells type (18650, 20700 or 21700) are widely used in battery packs for EV, mobility and storage applications.
Page also available as download : Accelonix Battery Bonding information and solutions brochure![]()
How does wire bonding works?
Wire-bonding (Ultrasonic Compression bonding) is a combination of three precise controlled parameters that form the bonding: 1.Ultrasonic vibrational power 2. Downward force 3. Time
Typically during battery bonding the wire is pushed by means of a wedgetool and with a controlled force against the surface to be bonded, then the wire is vibrated at 60 kilo Hertz for 100 millisecond.
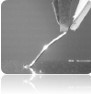


Advantages Wire bonding vs spot or laser welding.
Fusing Wires: Wire act as a fuse, if a cell fails it will be isolated from the pack and the pack will continue to function.
The pack is not destroyed by a meltdown and will be fixable, and there is no danger to life from a simple cell failure.
No Heat: Heat is dangerous for an 18650 cell. No heat is used in ultrasonic compression bonding, unlike other methods such as spot or laser welding. Only limited heat is generated by the friction which is very local and only on the outer skin of the surface.
Clean Process: Wire bonding is a clean process and generates no sparks, residue materials or other possible contaminations, so no cleanup after.
Height: Wire bonding machines are capable of bonding in height variations, the cell and bus bar can be in a different height. Next to that wire bonding machines give full control on the final loop shape design.
Testability: Wire bonds are easy to test on bond strength to ensure highest quality requirements. Unlike spotwelds, which are hard to test and notorious for contact failure over time.
Flexibility: Wire Bonds have some flexibility due to their wire loopshape and material properties , in case of a pack flex deformation they will not break. Spotwelded packs are not flexible which makes the connections easier to break.
Automation: Wire bonding allows full automation of the bonding process with CNC machines for higher efficiency, quality and decrease in the amount of manual handling.
Materials of busbars
Busbars are what connect the cells together in series. The question is from what conductive material (sheetmetal) to lasercut the busbars: Nickel, Copper or Aluminum?
Mechanically, busbars for the battery pack of EVs/HEVs must be durable, capable of withstanding high levels of vibration while simultaneously providing rigidity to keep the integrity of the battery module assembly.
Electrically, connections must handle high current coming from the cells but also increasing voltage levels as future cells will be up to 5.0V per cell. As a result, the impact on the clearance and creepage distance for the electrical insulation will be significant. The performance of the connections depends also upon the composite materials used to construct the busbars.
Nickel is not the ideal electrical conductor, and is historically used only because it is easy to robot spot-weld. When it comes to conducting high current, aluminum and copper are better options.
Copper has the best electrical conductivity, best thermal conductivity and lowest thermal expansion. But on the downside copper will oxidize very fast due to its exposure to air. (A layer of oxidation on bonding surfaces has a strong negative effect on the bonding quality and bondability)
Aluminum is over twice as conductive then Nickel, less sensitive to oxidation then copper, less costly and lighter in weight then copper. Aluminum is often the best overall choice, and copper would be our choice in packs were spaces are tight.
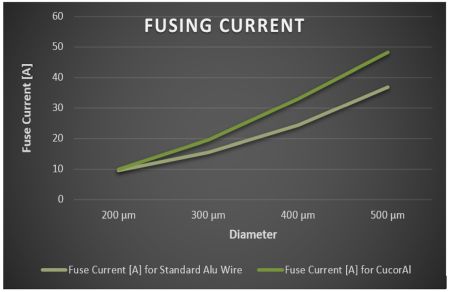
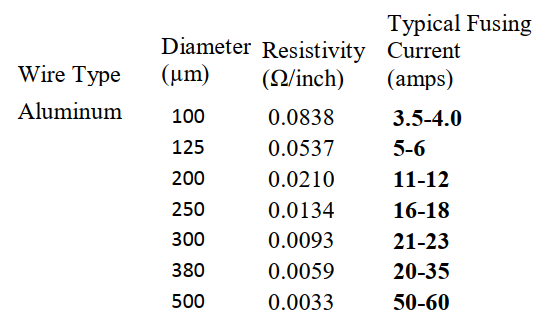
Fusing Wires
The fusing behavior of wires is mainly depending on material, diameter and length of the wire.
Below fusing current table of Aluminium wires.
Manual (Semi-Automatic) Battery Wire Bonding Solutions

- Manual (Semi-Aautomatic) Heavy Wire Bonder for wires Ø 100µm to 500µm
- Tabltetop system for development, proto and low volume production
- Semi automatic, motorized y & Z axis, height sense and programmable loop profiles
- Easy to use solution with digital touchscreen interface and program storage
- German built high quality system, full local process support by Accelonix engineers
- For more information and product brochure please visit the productpage : TPT HB30 Heavy Wire Bonder
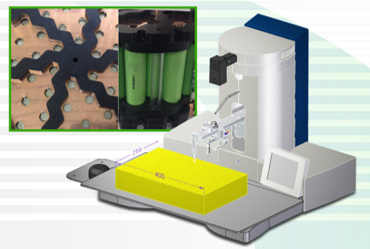
Automatic Wire Bonding Solutions

- High speed full automatic Heavy Wire Bonders
- Largest working araes in the market up top 700 X 1132 mm
- Single bondhead can handle wires from Ø 50µm to 600µm
- Automation : Manual batch loading or Fully automated inline operation.
- Bondhead with non-destructive pulltest & Piqc sensor for 100% quality monitoring in real-time
- German built high quality system, full local process support by Accelonix engineers
- For more information and product brochure please visit the productpage : Hesse Heavy Wire Bonders

Page also available as download : Accelonix Battery Bonding information and solutions brochure![]()





















